Confused about what peptides really are, and how they can prove beneficial to your health and well-being?
It has come to our attention that a lot of people don’t have the slightest clue what peptides are, even though it’s been around since the 1920s, are present in most foods we eat, and can even be found inside our bodies.
This article will explain everything you’ll need to know about peptides – what they are, how they work, their role, and outline their potential benefits and side effects.
What are Peptides?
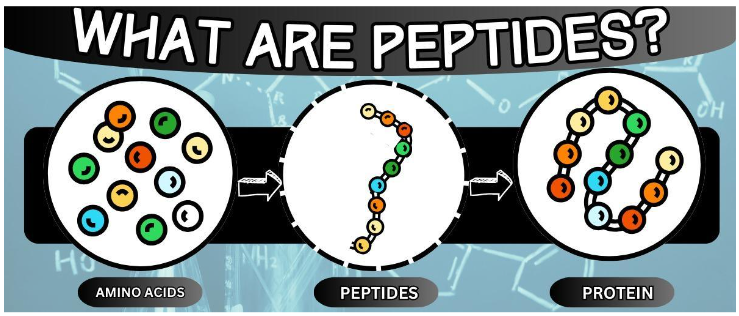
Peptides are essentially defined as strings of molecules called “amino acids”, which form proteins when combined with other amino acids through a peptide bond.
Peptide bonds form when one amino acid links together with another one, creating a chemical reaction that releases water, forming a peptide. For a more in-depth understanding of how these bonds form, here’s a perfectly good YouTube video to explain it:
Before we go into detail about how peptides work and how they are used, we first need to address what an amino acid is.
Amino Acids
Amino acids are molecules that are essential for various functions in the body. When one or more chains of amino acids are strung together in specific sequences, they become the “building blocks” of different types of proteins.
These proteins are responsible for properly performing vital body functions such as breaking down food to release energy, repairing damaged tissue, and supporting growth.
While both peptides and proteins are comprised of bonded amino acids, they are differentiated by how long they are.
Peptides can be classified as more of a “short version” of proteins since they only contain about 2-50 amino acids, while proteins can contain more than 50 amino acids
How Peptides Work
In simple terms, peptides function as your body’s “signals” that tell your cells what to do. They influence most of your body’s major biological processes such as the following:
- immune system regulation
- Natural growth hormone release, also known as (GHRH)
- extracellular matrix production
- nerve cell growth and migration, to name a few.
Thanks to this multifunctional nature, researchers have been studying and developing peptide hormones to help treat various medical conditions.
A popular example that’s been around since 1921 is insulin. This 51-amino-acid-long hormone was the first synthetic peptide ever produced in a lab.
Insulin is widely known for its role in helping your cells regulate glucose levels (the sugar you get from eating food) and liver, muscles, and adipose tissue and has been used to treat diabetes mellitus type-1 patients two years after its discovery.
What Makes Peptides so Popular?
Thanks to several decades of thorough research, peptides are now emerging as a promising option to both scientists and healthcare practitioners, as they provide several health benefits.
To give you a gist of its prevalence, there have been over 21,000 peptide-related studies (and counting) in 2024 alone. To illustrate this trend, here’s a data chart to fully represent the growing interest in peptide research.
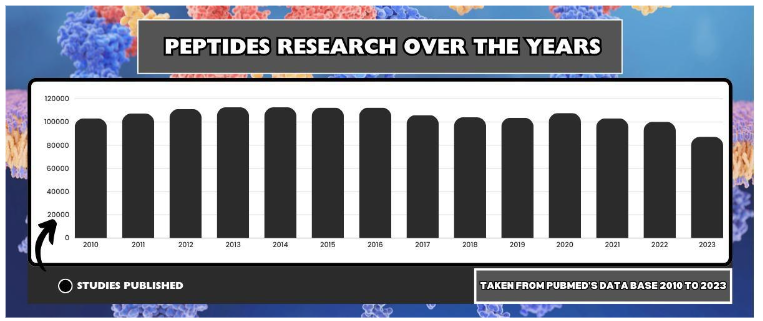
Body functions such as regulating your immune system and aging process, reducing inflammation, stimulating wound healing, and improving cognitive functions are made easier with the help of peptides.
Pretty cool, right?
Health Benefits
When compared to traditional methods, peptides are becoming an increasingly popular option to the public because they are easier to consume (either orally or topically), have fewer side effects, and the byproducts they produce can be naturally recycled by our bodies.
Numerous animal and human-based research over the years also show that peptides can grant you a plethora of beneficial effects such as the following:
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Enhanced bone strength and density
- Accelerate tissue healing, with BPC-157
- Increased muscle strength
- Better skin elasticity
- Promote fat los, with Tesofensine
A perfect example to showcase this is BPC-157.
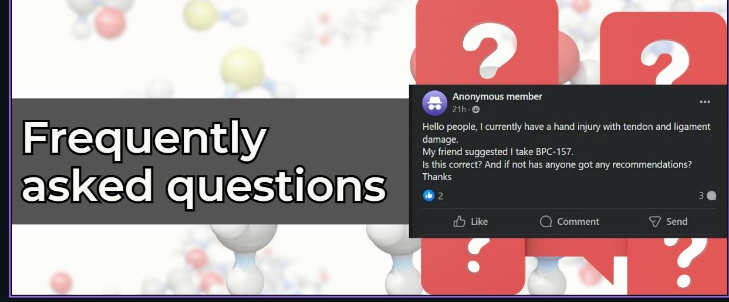
https://www.facebook.com/groups/sarms.peptides.nootropics/permalink/1542021393319919/
Let’s use this question posted by an anonymous member we found in a Facebook group called SARMs & Peptides & Nootropics.
To fill you in, BPC-157 is this really awesome peptide already present in your gut and its primary benefit is quick healing, but its effects can also extend to reduce pain and improve muscle function.
This peptide is so good at healing and recovery that it has been dubbed the “Wolverine peptide” by the fitness and wellness community due to how effective it is in doing its job.
Oh yeah, we need to answer this guy’s question – his friend is correct.
According to this 2019 study, BPC-157 promotes healing in tendons and ligaments by accelerating tissue repair. If this person’s hand injury also tore up any muscles, BPC-157 can also help reduce scarring and improve function post-injury.
Side Effects
According to WebMD, unless you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, taking other medications, and/or have a medical condition, peptides are generally considered safe when used under the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider.
Additionally, they are highly unlikely to cause serious side effects since peptides are also present in most foods we normally eat and our body breaks them down into amino acids.
According to a randomized controlled trial to study the effectiveness of collagen hydrolysate (CH) peptides on the skin, the researchers failed to note any side effects among the 69 female participants throughout the 8-week study.
However, like any other substance, overuse of peptides can lead to adverse side effects that may include but are not limited to the following:
- Increased appetite (if you consumed MK-677)
- Allergic reactions
- Dry mouth
- Tingling or numbness
- High blood pressure
- Headaches, dizziness, and fatigue
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
To avoid such side effects, it’s always advisable to consult this matter with your trusted healthcare provider before using any peptide supplements/topical products.
Key Takeaways – Should You Use Peptides?
In short, peptides are amino acid chains that influence a lot of your body functions. Natural processes such as your metabolism, body composition (i.e. hormones, immune system), cognitive function, and cell growth are regulated by these compounds.
For all that it’s worth, peptides are a hot topic right now – many people think so too.
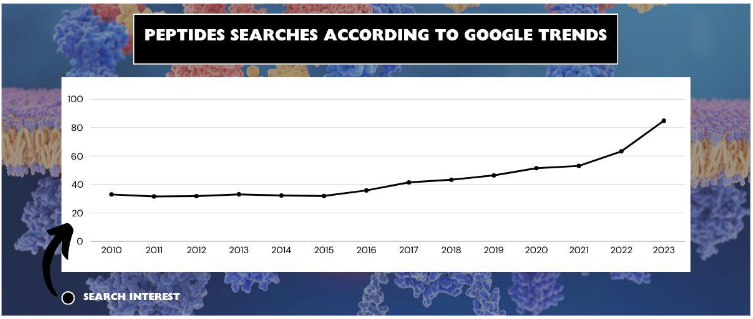
According to Google Trends, there’s been a growing interest in peptides in recent years. While we do not know what is the exact cause for this trend, what we do know is that it’s possibly due to their therapeutic applications.
So, should you consider using peptides? Absolutely – you’re missing out if you aren’t.
However, take it with a grain of salt – peptides aren’t magic beans ready to solve all health conditions, but peptides are phenomenal tools when combined with proper medical guidance.
frequently asked quentions
Are peptides legal?
Yes, peptides are legal in the US as long as they are used exclusively for in-vitro research purposes. In-vitro studies (Latin: “in glass”) are studies performed outside of a living being. Regulations for peptide products are overseen by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Why peptides are banned?
On October 6, 2023, the FDA updated its list of bulk drug substances under section 503A – taking some peptide substances off the shelves for compounding pharmacies.
While this sounds like peptides are getting banned, in reality, the FDA just made it harder for doctors to legally prescribe you peptides from your compounding pharmacy.
Will peptides build muscle?
Absolutely. Specific peptides such as MK-677 are wildly popular with the fitness community since they stimulate certain hormone production such as the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and human growth hormone (HGH).
Are peptides steroids?
No, peptides and steroids are distinct compounds – they are comprised of completely different molecules.
According to WebMD, peptides are amino acid chains, whereas steroids are fatty molecules shaped like a ring. While both of these compounds can help you build muscle and contribute to fat loss, steroids often have serious side effects when compared to peptides.
Can peptides cause cancer?
No, peptides cannot cause cancer, but if you already have cancer – certain peptides that contain HGH can accelerate it.
HGH is a peptide that stimulates the pituitary gland to produce more IGF-1, which in turn helps thicken and elongate bones, grow muscle, and reduce fat.
However, too much IGF-1 can promote cancer growth by hampering apoptosis (cell death) and boosting cancer cell proliferation.
Any idea where peptides come from?
There are two types of peptides: endogenous peptides and exogenous peptides.
Endogenous peptides are naturally produced in the human body. Examples of endogenous peptides include endorphins, enkephalins, dynorphins, and nociceptins.
On the other hand, exogenous peptides enter our bodies through food, supplements, and/or medications.
Food sources such as eggs, milk, beans, and meat contain these peptides. Additionally, common examples of exogenous peptides found in supplements and medications include collagen, which is widely used in the skin industry, and creatine for the fitness industry.






